HOME
The Marvelous World of Cảbon

As the sixth component on the list of elements, cảbon is an exceptionally versatile fundamental component for every phase of life. Carbon is a complex component with various applications and forms; this article will cover those uses and forms, alongside carbon’s primary location in the universe of nature and its effects on people’s lives.
1.The Role of Carbon in Nature
Carbon Cycle: A Dance of Elements
The intriguing carbon cycle is at the centre of the biological system; it involves the movement of cảbon through the air, water, land, and all forms of life. The delicate equilibrium of our earth is maintained by this carbon cyclical dance.
Importance in Photosynthesis
Among carbon’s most important functions is its participation in photosynthesis, the transformation of carbon dioxide into oxygen and glucose by plants. Not only does this process keep plants alive, but it also makes the oxygen that we breathe.
2.Forms of Carbon
Elemental, Organic, and Inorganic
The basic black carbon and the complex organic molecules included in living things are two of the many shapes cảbon may take. In order to make sense of the many ways carbon shows itself in nature, it is essential to understand these forms.
Elemental Carbon
There are three distinct forms of cảbon, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and they include graphite, coal, and diamonds.
Organic Carbon
Organic carbon, which is present in all forms of life, is essential for survival. It is the building block of all biological molecules, from DNA to carbs.
Inorganic Carbon
Although carbonates and other inorganic cảbon compounds get all the attention, they are just as important, particularly in geological processes.
3.Carbon in Daily Life
Carbon-Based Products
From the rubber in our tyres to the plastic containers we use every day, carbon-derived items are all around us. The pervasiveness of cảbon can be better understood by identifying these commonplace things.
Carbon Footprint
For environmental consciousness, knowing one’s own carbon footprint is essential. Our carbon footprints are affected by everything we do, from how we travel to how much energy we use.
4.The Environmental Impact of Carbon
Carbon Emissions: The Culprit Behind Climate Change
The element carbon dioxide is emitted into our atmosphere when fossil fuels undergo combustion, which contributes to the heating of the planet and the greenhouse effect. Global warming as well as other climate change occurrences are obvious outcomes of unchecked greenhouse gas emissions.
Global Warming
Growing cảbon emissions are contributing to temperatures around the globe to rise, resulting in catastrophic impacts on ecological systems, weather trends, and sea levels. Reduced carbon dioxide emissions must be the number one objective if we are to combat the impact of climate change.
5.Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
Technology Overview
Carbon capture and storage, also known as CCS, is a fresh and intriguing technology with considerable promise in helping to fight against global warming. It involves minimizing the emission of carbon dioxide into the earth’s atmosphere by storing the greenhouse gasses underground following which it has been absorbed from manufacturing operations.
Benefits and Challenges
Although CCS presents an opportunity to lessen cảbon emissions, obstacles including expensive prices and lack of public support must be overcome. For widespread acceptance, it is necessary to balance the benefits and challenges.
6.Carbon Trading
Concept
One novel strategy for reducing emissions of carbon is carbon trading. Carbon allowances are allotted to businesses, and those who have extra can sell them to those that are using more than they can. This system encourages lowering emissions through the use of market forces.
Market Dynamics
One way to understand the economic forces at work in environmental sustainability is to look at the carbon trading market and how it operates. It exemplifies how monetary incentives may be congruent with environmental objectives.
7.Innovations in Carbon Reduction
Sustainable Practices
Sustainable practices strive to reduce environmental impacts through the use of renewable energy sources and environmentally friendly production techniques. These endeavors demonstrate the possibility of a balanced relationship between human actions and the natural world.
Technological Advancements
State-of-the-art innovations, such air cảbon capture and the creation of carbon-neutral materials, demonstrate the progress being achieved in the fight against cảbon emissions. The future of sustainability is in these innovations.
8.Future Outlook of Carbon Management
Research and Development
The hunt for innovative approaches to carbon management is an ongoing area of research and development. Finding novel materials, improving current methods, and investigating cutting-edge technology are all part of this effort to lessen our dependence on carbon-intensive processes.
Global Initiatives
The importance of quickly resolving issues connected to carbon has been highlighted by international cooperation and agreements. Everyone is pulling together, from the Paris Agreement to smaller-scale efforts, to reduce carbon’s negative effects on Earth.
9.Conclusion
Cảbon is an essential thread that runs through the vast fabric of our lives, linking the natural world with human activity and commerce. A sustainable and prosperous future depends on our ability to acknowledge its importance and carefully manage its influence.
10.FAQs
1.How does carbon impact climate change?
The greenhouse effect is an essential component of climate change, and cảbon, specifically carbon dioxide, plays a role in the phenomenon by absorbing heat through the planet’s atmosphere and causing climate change.
2.What are some common carbon-based products?
Products that are often made from cảbon include things like plastics, rubber, textiles, and fossil fuels.
3.How does carbon capture and storage work?
The idea of “carbon collection and storage” refers to the practice of avoiding environmental release of greenhouse gasses such as carbon dioxide by removing it from manufacturing processes and depositing it.
4.Can individuals reduce their carbon footprint?
Using energy that is renewable, cutting down on trash, and purchasing eco-friendly items are a few examples of sustainable practices that people may employ in order to reduce their impact on the world around them.
5.What is the significance of carbon trading?
By creating a market-driven incentive for businesses to reduce their cảbon emissions, cảbon trading helps strike a balance between economic growth and ecological preservation.
HOME
Rebeldemente: Embracing the Spirit of Rebellion

As an emblem of rebellion and uniqueness, the phrase “rebeldemente” stands out in a society that frequently promotes equality. From historical viewpoints to its modern-day expressions across several domains, this essay delves into the complex nature of revolt.
Introduction
“Rebeldemente” is really about refusing to conform and standing up for what you believe in. This word, which conjures images of defiance, questions established standards and exhorts people to value their own opinions. Throughout history, rebellion has been a defining factor in many fields, including politics, art, music, and personal growth.
Historical Perspectives on Rebellion
There are numerous examples throughout history of rebellion leading to major social upheavals, ranging from ancient revolts to contemporary revolutions. Examples of successful uprisings that pushed back against tyrannical regimes and brought about positive change include the Boston Tea Party, the French Revolution, and the Civil Rights Movement.
Modern Manifestations of Rebeldemente
There are many different kinds of rebellion in today’s culture. Embracing unique expressions and questioning traditional standards, fashion, and lifestyle trends frequently mirror a defiant attitude. When it comes to revolt and the amplification of voices calling for change, social media platforms have become potent weapons.
Rebellion in Personal Development
Disregarding the negative associations commonly linked with defiance, it has the potential to spur individual development. Adopting a defiant attitude enables people to challenge conventional norms, which opens doors to discovering oneself and being genuine.
Artistic Expression of Rebellion
Rebellion has always been a powerful symbol for artists and authors to express their disapproval or challenge. Creative expression becomes a potent means of communicating defiance, whether in literature that challenges authority or in the visual arts that portray social turmoil.
Music and Rebellion
One of the main reasons why people have rebelled is because music is a worldwide language. Inspiring change and encapsulating the spirit of defiance, iconic songs frequently function as anthems for political and social movements.
Political Rebellion
When it comes to politics, rebellion may either bring about beneficial change or cause chaos. Uprisings against repressive political systems are crucial, as seen in the Arab Spring and the struggle against apartheid.
Rebellion in the Workplace
Despite its negative connotation, disobedience may be an asset in the workplace. Workplaces that foster innovation and question established corporate structures tend to be more agile and responsive to change.
Impact of Rebellion on Society
Rebellion has far-reaching effects on society, changing cultural norms and the way things evolve. To grasp the bigger picture, it’s necessary to look at the good and bad effects.
Navigating Challenges in Rebeldemente
Rebellion, however potent, is not without its difficulties. If we want to prevent pointless disputes and make sure things work out well, we need to find a happy medium between being stubborn and actively participating.
Cultural Icons of Rebeldemente
Some people represent defiance at its finest; they go on to become icons in popular culture, encouraging people to be themselves. These revolutionary artists and activists shake things up and make a lasting impression on our culture.
Educational Approaches to Encourage Rebeldemente
Allowing pupils to think creatively and critically is a vital component of cultivating a revolutionary attitude. Individuals have a greater ability to succeed in a society that encourages creativity if they are open to new ideas and pushed to think for themself.
Rebellion as a Cultural Phenomenon
There is no denying the inseparable link between cultural progress and revolt. Reflecting the ever-changing nature of human advancement, cultural landscapes transform as societal norms undergo shifts in response to rebellious movements.
Media’s Role in Shaping Rebeldemente
A person’s view of rebellion may be significantly influenced by both conventional and digital media. Its depiction has the power to either encourage or discourage defiance, shaping how people in society view and react to criticism.
Conclusion
Rebellion is a brave, innovative, and progressive thread in the human experience tapestry. If you want to shake things up and find your way, “Rebeldemente” is the song for you. Adopting a rebellious mindset is more than simply being defiant; it’s a statement of identity that adds to the diverse fabric of human history.
FAQs
Is rebellion always a positive force?
The results of a rebellion, depending on the circumstances and tactics used, might be good or bad.
How can one embrace a rebellious mindset in a professional setting?
It is crucial to strike a balance between innovation and preserving corporate structure. Keep an optimistic attitude and strive for improvements.
Are there historical figures who embody the spirit of rebellion?
Certain individuals look up to people like Frida Kahlo, the late Nelson Mandela, and Martin Luther King Jr. as icons of struggle.
Can rebellion be taught in educational settings?
Children may indeed develop a rebellious spirit via an educational system that values critical thinking and creativity.
How does the media influence perceptions of rebellion?
The media has the power to influence how society views dissent by amplifying or downplaying narratives of rebellion.
HOME
Unlocking Your Memory Potential with the “Four Digits to Memorize NYT” Technique

Having the capacity to commit important knowledge to memory is priceless in a world where information is abundant. Mastering the skill of memorizing may greatly improve one’s cognitive abilities and productivity, whether one is trying to recall crucial dates, phone numbers, or even full passages of literature. The “four digits to memorize NYT” method is an interesting approach that is becoming popular in memory-enhancing circles. How may this technique change the way you think about memory? Let’s take a closer look at what it involves.
What is the “Four Digits to Memorize NYT” Technique?
For easier memorization of a lengthy string of numbers, try the mnemonic trick known as the “four digits to memorize NYT” approach. Created by memory specialists and made famous by outlets like The New York Times, this method streamlines numerical sequence encoding and recall by dividing them into smaller, more manageable pieces.
How Does it Work?
Essentially, the “four digits to memorize NYT” method makes use of the brain’s natural ability to recognize and associate patterns. Customers are advised to cluster sets of four numbers rather than trying to memorize long strings of numbers sequentially. Individuals can construct memorable mental cues that aid memory by attributing meaning or images to each group.
Steps to Effectively Use the Technique
- Understanding the Technique: Get to know the method’s foundational concepts, like as chunking and visualization.
- Practice and Repetition: As you gain experience, start with easier number sequences and work your way up to more difficult ones. The secret to fully internalizing the approach is consistent practice.
Advantages of Using this Method
Among the many benefits of the “four digits to memorize NYT” method are:
- Efficiency: This strategy simplifies memory by reducing big numbers to smaller ones.
- Retention: Making use of strong mental images and meaningful connections helps people remember what they’ve learned for longer.
- Versatility: In addition to numbers, this method is quite versatile and may be used to learn names, dates, and even full speeches.
Real-Life Applications and Examples
Everyone from test-takers to service providers who need to commit client codes to memory has benefited from the “four digits to memorize NYT” method. Take into account the following situations:
- An approaching test requires the student to memorize mathematical formulae.
- During a presentation, a high-ranking executive recalls important financial data.
- An enthusiastic language learner working to memorize new terms.
Tips for Enhancing Memorization Skills
Listed below are some suggestions for making the most of the “four digits to memorize NYT” method:
- Create Vivid Mental Images: Visualize Each Set of Digits as an Individual Scene or Image: This will Help You Recall Them Better.
- Utilize Repetition: To Strengthen Memory Retention, Review the Encoded Information Regularly.
- Associate with Personal Experiences: To enhance their memorability, connect the number sequences to relatable situations or stories.
Challenges and Limitations of the Method
Despite its effectiveness, the “four digits to memorize NYT” method also has its drawbacks. Some people could have trouble with:
- Initial Learning Curve: Time and effort are required to master the process, particularly for individuals who are not experienced with mnemonic techniques.
- Limited Applicability: While this method works well with numerical data, it might not be the best fit for other kinds of information.
- Potential Overreliance: Relying too much on mnemonic methods could eventually impede the development of spontaneous memory.
Comparison with Other Memorization Techniques
The “four digits to memorize NYT” method provides a novel combination of ease of use and efficacy when compared to conventional rote memory and other mnemonic techniques. This strategy takes advantage of the brain’s inherent tendency towards seeing patterns and patterns rather than relying just on repetition, which is the focus of other approaches.
Expert Opinions and Testimonials
As a powerful tool for improving cognitive function and academic achievement, the “four digits to memorize NYT” strategy has the support of many memory scientists and educators. User reviews confirm its usefulness in a variety of contexts, from lecture halls to corporate executive suites.
Conclusion
Having good memorization and recall skills is important in this day of information overload. For speedy and realistic results while learning number sequences and more, use the “four digits to memorize NYT” method. People may reach new levels of cognitive ability and unleash their memory potential by using chunking, imagery, and association.
FAQs
Is the “four digits to memorize NYT” technique suitable for children?
Yes, this method can help kids learn, particularly when it comes to arithmetic and history.
Can I use this method to memorize entire passages of text?
Although it was originally developed for numerical data, some users have modified it to memorize language by substituting numerical values for words.
How long does it take to see results with this method?
Learning styles and habits of practice can affect the outcomes. Memorization may be improved significantly in just a few weeks with constant practice.
Are there any online resources or apps available to aid in learning this technique?
The “four digits to memorize NYT” approach is only one of several mnemonic methods that can be learned and used through a variety of online resources and smartphone apps.
Can this method help with short-term memory loss or cognitive decline?
People with severe cognitive impairment should talk to doctors about individualized treatments and assistance, even if mnemonic strategies can help with memory improvement.
HOME
Unveiling the Beauty of Lillyflower2003: A Comprehensive Guide

Among the many examples of artistic genius seen on the Internet, Lillyflower2003 shines out. This article dives into the fascinating universe of Lillyflower 2003, investigating where the artist came from, what she draws inspiration from, and the many works that have won her fans over. Come along as we dive into the mystery of Lillyflower 2003’s rise to fame in the internet art world and find out what the name means.
Who is Lillyflower2003?
Someone with boundless imagination and talent goes by the internet identity Lillyflower2003. As a result of their one-of-a-kind combination of talents and distinctive style, Lillyflower2003 has established itself in several online spaces, making a lasting impression on anybody who comes across their creations.
Origins and Evolution
To truly appreciate Lillyflower 2003’s artistic journey, one must know where they came from. Beginning as an introspective investigation, Lillyflower2003’s path eventually flowered into a public display of skill in visual art, literature, and other kinds of expression. We may better understand the roots that formed Lillyflower2003’s distinctive creative persona if we delve into the early inspirations and landmarks.
Exploring Lillyflower2003’s Creations
Visual Art
The visual art of Lillyflower 2003 is an enchanting web of forms, hues, and feelings. The artist’s inventiveness is on full display in every work, from detailed digital graphics to atmospheric paintings. The visual art of Lillyflower 2003 is defined by several factors, some of which will be discussed here.
Written Works
When it comes to writing, Lillyflower2003 is just as skilled as she is on canvas. The written portfolio of Lillyflower 2003 is a veritable treasure mine of engaging writing, intriguing poetry, and thought-provoking storytelling. Learn the meaning behind these words, where they came from, and the influence they have on readers.
Collaborations and Community
Building strong communities is one of Lillyflower2003’s strongest points. There is a thriving ecosystem around Lillyflower2003’s creations thanks to her collaborations with other artists, her involvement in online competitions, and her connection with fans. Find out how Lillyflower2003 and other creatives have worked together to benefit the community at large.
Behind the Scenes: Lillyflower2003’s Creative Process
Exploring how Lillyflower2003 comes up with her ideas gives us a look into her head. Anyone interested in art or design would benefit from knowing more about the creative process, from the first ideas to the last touches.
The Impact of Lillyflower2003
There is a real-world influence to Lillyflower2003 that goes beyond just the digital canvas and written word. The impact of Lillyflower2003’s work is seen in the testimonies of those who have worked with and admired her. This impact may have been inspirational, encouraging, or in creating a feeling of community among creatives.
Conclusion
With her masterful blending of visual and linguistic miracles, Lillyflower2003 stands out in the vast realm of online creativity. Readers are invited to immerse themselves in the magical universe created by this remarkable artist, Lillyflower2003, as this thorough guide has offered an insight into her origins, growth, and effect. The adventure is far from ended, with the promise of much more creative marvels to come, as Lillyflower2003 keeps captivating and inspiring.
FAQs
Lillyflower2003, who is she?
A talented individual artist with a huge influence within the online creative world goes by the username Lillyflower2003 on the internet. Lillyflower 2003 has risen to notoriety in the realm of online art due to its mesmerizing visual art, intriguing textual works, and enthusiastic participation in social networks.
What inspires Lillyflower2003’s creations?
Nature, which is feelings, life events, and an extensive variety of creative and literary works are just a few of the numerous places that Lillyflower2003 finds inspiration. Their artistic inventory is defined by its diverse and complex tapestry, which has been enhanced by this eclectic assortment of ideas.
How can I view Lillyflower 2003’s work?
The artist known as Lillyflower2003 frequently posts their works on several websites, art forums, and social networking sites. To keep up with their most recent announcements and creations, follow their official accounts and profiles.
Is Lillyflower 2003 available for commissions or collaborations?
Lillyflower 2003 is no different from the many artists that get their inspiration from collaborating. You may find out about commissions or joint projects by following their social media accounts. The contact information usually given on their main channels can be used to make direct questions.
What tools or software does Lillyflower2003 use for their digital art?
While everyone’s creative process is unique, Lillyflower2003 frequently discusses the digital tools they use most. To understand how Lillyflower2003 achieves her one-of-a-kind style, you should hunt for “behind-the-scenes” information or artist profiles.
-

 TECH8 months ago
TECH8 months agoExploring the Exciting Features of PHP Version 8.1 for Enhanced Web Development
-

 CRYPTO4 months ago
CRYPTO4 months agoUnlocking the Potential: Understanding WalletConnect là gì
-

 NEWS5 months ago
NEWS5 months agoBestadvise4u.com News: Your Gateway to Informed Living
-

 ENTERTAINMENT5 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT5 months ago“кинокрадко” – Unmasking the Culprit Behind Film Piracy
-

 TECH4 months ago
TECH4 months ago“몽세리 266b+v”: Revolutionizing Technology for a Better Future
-
 HEALTH6 months ago
HEALTH6 months agoTough Tissue Muscle Connector: The Unsung Heroes of Movement
-
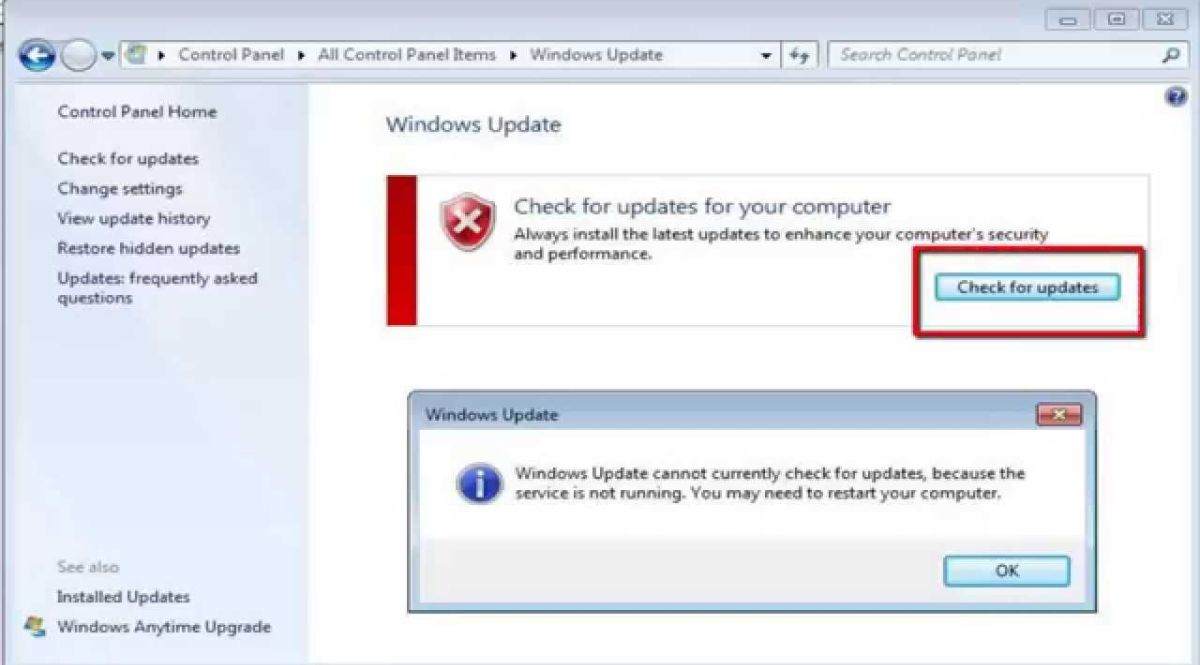
 WINDOWS11 years ago
WINDOWS11 years ago(solved)-Windows update cannot currently check for updates, because the service is not running. You may need to restart your computer
-
 WINDOWS9 years ago
WINDOWS9 years ago(Solved) – “How do you want to open this type of file (.js)?” Windows 8/8.1
